New Oriental’s Executive Summary
New Oriental Education & Tech Grp (New Oriental) is the largest provider of private educational services in China based on the number of program offerings, total student enrollments and geographic presence.
The company offers a wide range of educational programs, services and products, consisting primarily of language training and test preparation, primary and secondary school education, online education, content development and distribution, overseas study consulting services, pre-school education and study tour.
The company provides educational services primarily under the “New Oriental” brand, which is the leading consumer brand in China’s private education sector. (ref: annual report)
Below, we summarized 6 important points from the company that investors can take away.
#1 Market reactions to Q1 earnings miss & recent regulations made the price more reasonable but still need to wait for good buy in opportunity.
New oriental reported adjusted Q1 earnings missed estimates and issued downside revenue guidance for Q2. The disappointment and recent two regulations put downward pressure on the equity price.
The ambiguity and uncertainty in the regulations spooked the market and caused shares of oversea-listed Chinese education companies plunged for more than two months including New Oriental. However, the two regulations put pressure on company’s revenue & earning expectation but can also have positive effect on sector further consolidation and benefit the company.
Although current equity price is half the peak level, investors still need to wait for good buy in opportunity. P/E-based valuation and DCF valuation methods give a target price of USD $55.
#2 Defensive investing nature and rapidly growing sector.
The private education sector in China has a defensive investing nature and is rapidly evolving, fast growing and highly fragmental and competitive.
New Oriental Education (EDU) is the leader and largest tutoring company in China with a superior brand recognition. K-12 is one of the fastest growing sub-sectors in the private education but with strong competitors such as TAL Education Group.
#3 Prepaid business model and strong cash flows.
Educational programs and services has a typical prepaid business model which guarantees solid cash flow.
After 25 years, New Oriental has entered a very mature stage with strong cash flow and financial status.
#4 Diversified products and reliable management.
New Oriental has successfully expanded into multiple sub-sectors, including K-12, one of the fastest growing segments.
The company also has a good track record of trustful and ethical management.
#5 Leading edge in online education sector and control of one of the leading online education company Koolearn which is queuing for HK IPO.
Koolearn technology holding limited (Koolearn) is the online subsidiary of New Oriental. The company is the leader in China online education sector and the only public company which realizes sizeable revenue and profit.
By holding Koolearn, New Oriental can open enormous online education market size and sustain its growth rate.
#6 Major Downside Risks
Major downside risks include
- Structural slowdown in target population growth and a faster-than-expected slowdown in the English tutoring market;
- Fierce competition from both offline and online players;
- Regulation and policy risks and
- Forex risk due to trade war disputes.
New Oriental’s Detailed Analysis
Intro on New Oriental Stock
In 1993, New Oriental Education & Tech Grp (“New Oriental”) was founded in Beijing by Yu Minhong. Because of the three founders’ teaching and oversea background, they spotted the first surge of studying abroad in the early 20th century and observed huge demand and supply gap in English preparation test market and caught this great opportunity.
Thus, in the very first beginning, the company focused on offering preparation courses on TOEFL, GRE and GMAT to Chinese students who wanted to study abroad. In the past 25 years New Oriental experienced high-speed growth, bottle neck, strategy adaption and 2nd round high growth and established the strong brand of “New Oriental”.
New Oriental Education & Tech Grp is the largest provider of private educational services in China based on the number of program offerings, total student enrollments and geographic presence. The company offers a wide range of educational programs, services and products, consisting primarily of language training and test preparation, primary and secondary school education, online education, content development and distribution, overseas study consulting services, pre-school education and study tour. The company provides educational services primarily under the “New Oriental” brand, which is the leading consumer brand in China’s private education sector. (ref: annual report)
As of 2016, New Oriental has built 67 short-time language educational schools, 20 book stores, 771 learning centers, and more than 5,000 third-party bookstores in 56 cities in China.
New Oriental has had over 26.6 million student enrollments, including over 1.3 million enrollments in the first quarter 2017. The company’s market capitalization was approximately USD 11.13 billion. (ref: wikipedia)
Industry overview
China private education sector
In China it is a deep-rooted belief that high education qualification is noble and glory for the whole family because studying is the most common way for people to get a good job then better society status, wealth and life. This belief has been enhanced by government policies and society changes in the past 40 years. Chinese government has implemented one child policy since 1980s which makes most family concentrate all the resource, disposable income, attention and expectation on the only child. The one child policy highly improves overall population’s education level and education household spending. Another important policy urbanization, although has nothing to do with education itself, results in great impact to education too. Large population flew into metropolitan cities, making competition fiercer. Parents living in metropolitan cities focus more on kids’ education due to better vision and personal life experience. On the other hand, education resources consolidated and concentrated further in major provinces and cities which make high quality education resource scarce to most people. In turn, this reality encourages Chinese parents spend more on children’s education.
Chinese government education spending reached above 4% of the country GDP in recent years. But comparing with developed countries, the education spending is 6.0% for USA, 5.5% for France and 5.3% for UK respectively. The public education spending needs to be raised further but It takes long term efforts which provides sizable potential room for private education development in China.
Private education industry market size
According to national population development plan, the population of China will reach 1.42 billion in 2020 and 1.45 billion in 2030. Total fertility rate (TFR) will rise from 1.55 in 2015 to 1.88 and maintain at this level. Population below 15 reached 0.233 billion in 2017.
The overall education sector in China is expected to be 6.78 trillion RMB in 2021 with a CAGR of 7.4% from 5.10 trillion RMB 2017 (source: MOE, National Bureau of Statistics and Bexcel Management). If further sector the overall education industry, based on information from MOE, National Bureau of Statistics, Bexcel Management and Frost & Sullivan, the detailed market size of major sectors are as follows:
Adult education has two major sub-sectors: language training and professional training. Language training shows stagnation trend in recent years due to several reasons: the number of enrolled college students has slowed down due to population structural change; the demand of language training has partially been satisfied by international schools since parents send their kids studying abroad at younger age.
The language training market is one of the first developed sub-sectors in China private education industry with much higher penetration & concentration rates. The professional training sub-sector, on the other hand, will likely enjoy resilient growth due to intense competition among professionals.
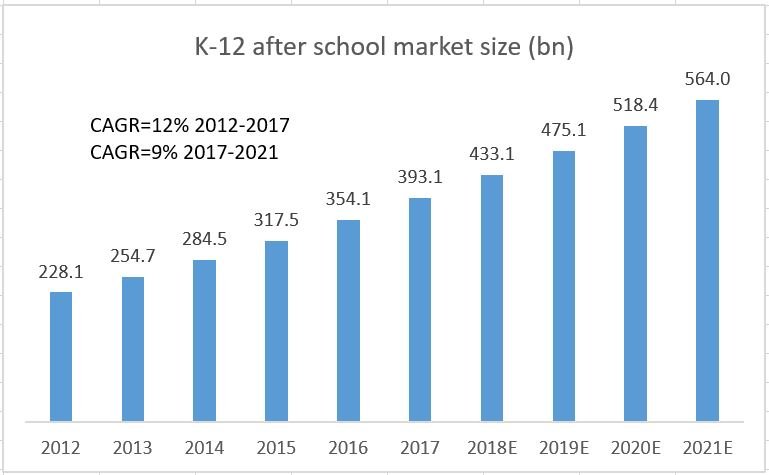
K-12 sector is the biggest portion in the China private education industry. However, the sector is highly fragmental and competitive. The market share of the four largest firms is less than 5%.
The market size increased from 228 billion in 2012 to 393 billion in 2017 with a CAGR of 12% and will continue to grow about 564 billion in 2021.
(Source: MOE, National Bureau of Statistics, Bexcel Management and Frost & Sullivan)
Junior English training courses and online education are the two sub-sectors with highest growth rate in China private education. Based on MOE, National Bureau of Statistics, Bexcel Management and Frost & Sullivan, the CAGR of Junior English training sector in 2011—2017 is 18.6% and will probably reach 24.0% in 2017 – 2021.
The market size is expected to grow from 102.8 billion RMB in 2017 to 239.8 billion RMB in 2021. The market size will double due to family disposable income increase and the universal two-child policy implementation. Within Junior English training sub-sector, English training for kids between 3 to 6 yrs is the fastest growing segment with an estimated CAGR of 27% plus.
Online education is not only disruption but also compliment of traditional offline education. Online education has unique advantages:
- it overcomes geography limitation and makes education resources available to way much more people nowadays;
- it provides great flexibility and turns over traditional education at fix time and place into on-demand format;
- it can also be repeated unlimited times and make education much cheaper.
However, online education has difficulty providing effective interaction between teachers and students and more suitable for adults rather than young kids with less self-discipline and attention span.
Based on MOE, Bexcel Management and Frost & Sullivan, the market size of online education has a CAGR of 28% in 2011—2017 and will continue to grow at a CAGR of 39% to reach 900 billion RMB in 2021. Players in this sub-sector can be further divided into content provider, platform and technology providers. Among the three, due to the nature of education, content provider has the best competitive advantage since customers put content quality priority.
Therefore, current big players in education sector have a natural advantage over others including internet giants with education ambition. Interestingly content providers with good brand name and internet giants become perfect partners and can set up joint venture to be more competitive in online education sub-sector.
(Source: MOE, National Bureau of Statistics, Bexcel Management and Frost & Sullivan)
Company Overview
Segment breakdown and key points
Since inception, New Oriental has grown rapidly and transformed from primarily a language training and test preparation company into the largest provider of private educational services in China. New Oriental program, service and product offerings are generally divided into 7 segments: test preparation; K-12 after-school tutoring; language training; primary and secondary schools; educational content, software and other technology development and distribution; online education; and other services and products. (ref: wikipedia & annual report)
Summary of key points:
- The private education sector in China has a defensive investing nature and is rapidly evolving, fast growing and highly fragmental and competitive. New Oriental Education (EDU) is the leader and largest tutoring company in China with a superior brand recognition in this sector.
- Educational programs and services has a typical prepaid business model which guarantees stable cash flows. After 25 years, New Oriental Education achieved US$1,799.5 million Revenue and US$274.5 million net income in the fiscal year ended May 31, 2017, representing a CAGR of 20.1% and 19.3% respectively for the past 3 years. The company has entered a very mature stage with strong cash flow and solid financials.
- New Oriental has successfully expanded into multiple sub-sectors, including K-12 sub-sector one of the fastest growing segments. The company has shown resilient growth, extensive horizontal expansion, capacity of innovation and sizable return to investors.
- Due to built-in vulnerability of the VIE structure and culture gap, it is extremely important for oversea listed Chinese company to have trustful and ethical leaders and management. New Oriental has a good track record in this aspect. And the management also shows willingness to return investors through special dividend or share buyback.
Mr. Michael Minhong Yu is the founder of New Oriental and has served as the chairman of the board of directors since 2001. He was also the chief executive officer from 2001 to September 2016.
In addition to his roles in the company, Mr. Yu also serves as vice chairman of the Beijing Young Entrepreneurs Association and vice chairman of the Committee of Education of the Central Committee of the China Democratic League.
Prior to founding the first school in 1993, Mr. Yu was an English instructor at Peking University from 1985 and 1991. Mr. Yu received his bachelor’s degree in English from Peking University. (ref: annual report)
- Long term strategy and diversified products
For products wise, New Oriental has penetrated from K-12 to adult training, covering from English to non-English, test related to non-test related extensive range of products. Sector wise, the company has business in tutoring, publishing, oversea study advisory and online education.
The company in the long run wants to build up an education ecosystem and become more resilience to different risks in the private education sector.
- Over reaction to the recent regulation incident in China
General Office of the State Council issued “opinions on rectification of all after-school training institutions” (the “Opinions “) on 22nd Aug 2018. The Ministry of Justice published the Circular seeking public comments on the Implementing Regulations of the Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Promotion of Private Education (Revised Draft) (Draft for Review) (the “Draft”) on 10th August 2018.
The ambiguity and uncertainty in the both regulations spooked the market and caused shares of oversea-listed Chinese education companies plunged for more than two months including New Oriental. However, the two regulations put pressure on company’s revenue & earning expectation but can also have positive effect on sector further consolidation and benefit the company.
Detailed segment analysis
Overseas English test preparation course
English preparation course is the starting point of New Oriental and where the company built up its brand “New Oriental”. The segment has been enlarged. According to iResearch the overall market size of language training reached 62 billion RMB in 2014 in which online language training takes 31.3%. The language training market is still quite fragmental with multiple major players. New Oriental is the biggest player with about 10% market share.
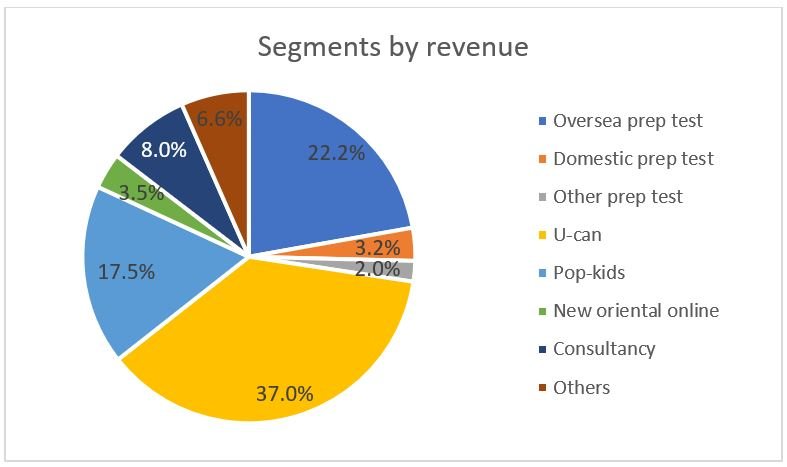
Although New Oriental has the absolute leading position and supreme brand, growth rate of revenue and profit in this segment is slowing down. As a direct result of growth rate of the total number of students studying abroad has slowed down. For year 2017, language training has taken about 27.5% of the total revenue.
(Source: Industrial securities and company information)
K-12 after-school tutoring services
New Oriental initially introduced an English after-school training programme for K-12 students in 2002. The company spun this programme into two separate brands in 2008: U-Can All Subjects (U-Can) for K7-12 students, and Pop Kids for K-6 children, both of which have expanded from English to all-subject tutoring, including English, Chinese and mathematics.
K-12 sub-sector is the cash cow and fastest growing segment, contributing about 54% to its total revenue. In 2016, New Oriental takes about 1.25% in overall K-12 sub-sector. It is expected to reach 13.64 billion RMB and New Oriental will take 1.68% K-12 market share. (source: Industrial securities) New Oriental believes the future growth potential of K-12 segment is huge and can even expect a CARG of 40-50% for the next 4 years (source: news editorial 2017). In 2017, revenue for Pop kids reached 315 million USD with a growth rate of 45.9% while revenue for U-Can reached 666 million USD with a growth rate of 31.7%.
Besides these two major brands, in 2007 New Oriental established kindergarten brand “New Oriental Stars”, providing international preschool education services. So far, New Oriental has 21 kindergartens in total. Kindergarten business will benefit first from loosening of one child policy. Thus, this segment is expected to grow fast too.
Online education
New Oriental set up its online education subsidiary in 2005, called Beijing New Oriental Xuncheng Network Technology Inc., owning and operating an online education platform, Koolearn.com. New Oriental online covers test preparation course, language training, K-12, 6 categories about 5400 courses in total.
In 2016, New Oriental online has registered users 13.5 mn and paid users 0.547 mn. Xuncheng has achieved a revenue of 334 mn RMB (2016) and 446 mn RMB (2017) with a profit of 59.55 mn RMB (2016) and 92.21 mn RMB (2017).
So far, New Oriental online is the biggest online education service provider in China with a market share of 0.63% (2017). The overall online education market is at very early stage and highly fragmental. New oriental has three strategies for its online business:
- (1) O2O integration;
- (2) further investment in its existing online platform, Koolearn.com; and
- (3) partnership with leading online players. (ref: credit-suisse)
New Oriental Stock Valuation Forecasts
Two valuation methodologies are used: P/E-based valuation and DCF valuation.
P/E-based valuation
The seven US-listed Chinese education companies are trading at an average of 46x CY17 P/E and expected 33x CY18E P/E.
Valuation comparison of education companies
The target price of US$55 is based on 29.2x FY19E EPS (USD $1.88), representing its 3 year historical average P/E level.
Sources: Wind, bloomberg and everbright securities. All market data is based on Oct 26th 2018.
DCF valuation
A discounted cash flow (DCF) financial model is used to calculate a target price of New Oriental. Assuming a WACC of 10% and a terminal growth rate of 2%, the base-case DCF valuation yields a target price of US$55 (round-up) by end-FY18.
For details of the DCF valuation, please refer to the excel financial model.
Key investment risks
Downside risks may emerge from:
- Structural slowdown in target population growth and a faster-than-expected slowdown in the English tutoring market
Due to structural population change, target student population growth will slow down. Plus, ages of Chinese students studying overseas become earlier. Thus, English test preparatory market and English tutoring market could slow down significantly.
- Fierce competition from both offline and online players (in the long run) and slower-than-expected growth in K-12 and online segments
China private education market is highly fragmental and competitive in all sub-sectors. Whether New Oriental sales and marketing strategy can result in decent expansion and growth is yet to be observed.
To maintain its leading market position, New Oriental should always put product quality, R&D and satisfying market evolving demand priority. Slow adaption to fast evolving changes and delays in R&D for better new programmes will have negatively effects on the company’s revenue and earnings.
More and more new entrants pop up in online education sub-sector. Enhanced competition put more pressure on the company. Slower-than-expected progress in this segment could undermine the company’s operating efficiency and profitability.
- Forex risk due to current trade dispute between China and USA
The current trade dispute between China and USA introduce greater volatility of exchange rate of CNY to USD. The depreciation of CNY could affect the company’s profitability.
- Regulation and policy risks
Regulation and policy changes of private education sector or examinations can substantially influence the company’s operation and expansion. Such changes can put large pressure on the company’s short-term revenue and profit.
How am I differentiated on New Oriental Stock
General Office of the State Council issued “opinions on rectification of all after-school training institutions” (the “Opinions “) on 22nd Aug 2018. The Ministry of Justice published the Circular seeking public comments on the Implementing Regulations of the Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Promotion of Private Education (Revised Draft) (Draft for Review) (the “Draft”) on 10th August 2018.
The ambiguity and uncertainty in the both regulations spooked the market and caused shares of oversea-listed Chinese education companies plunged for more than two months including New Oriental. The event is a typical demonstration how policy and regulation can influence share price of New Oriental and other Chinese education companies.
In the following part, major points about the Opinions and the Draft will be discussed.
Since New Oriental majority business is tutoring business, the Opinions have more effects on the Company. The uncertainty of the Draft is mainly on article 5, 12, 16 and 45:
Profit vs non-profit
The Draft has strengthened profit vs non-profit school criteria which indicates the government want to emphasize non-profit school’s nature as public welfare.
Profit school can focus more on earning returns. But private schools for compulsory education can only choose to be non-profit schools. However, the reality is most private schools didn’t declare either as profit or non-profit due to difficulty of implementation and lack of motivation to do so.
Therefore, unless detailed procedure and guideline is published otherwise the implementation will be in quite slow progress due to ambiguity.
VIE structure and strengthening of private education company expansion
Article 12 of the Draft states that “Education Groups” may not control non-profit private schools through merger and acquisition, franchising and contractual control. This article is the biggest uncertainty to private education companies.
First it puts a big question mark on VIE structure if contractual control refers to VIE. And what will happen to current VIE structured companies?
Second, schools for compulsory education (mainly primary and middle schools) are all non-profit. Does the article mean that such schools can only expand through endogenous growth instead of any kind of M&A?
However, there are no further explanation provided.
The uncertainty of the Opinion is mainly on:
Strengthening on requirements and contents
The Opinion details its requirements and make approval criteria and process stricter. The detailed requirements include:
minimum average area per student should be larger than 3 m2; pre-paid tuition fee can’t be charged for more than 3 months in advance; teacher certification is required for all tutors in major subjects; other requirements are also stated in fire protection, environment and sanitation. Among all these requirements, certification requirement is the most difficult to fulfill.
For example, according to Citi research, half tutors in TAL and New Oriental don’t have teacher certification. If tutors want to take the teacher certification examination, they have to take the exam in either household register location (户籍所在地) or personnel file location (人事档案所在地) which can be different from work location quite commonly. The negotiation whether there can a flexibility of examination location is still on-going between relevant companies and exam organization.
The Opinion also states detail requirements on tutoring contents, class size, content progress and allowable class time. These content requirements will strictly prohibit tutoring activities beyond the teaching syllabus.
Strengthening on requirements will be difficult and put pressure on all companies in the sector especially small median companies. And it will also raise the entry barrier for new tutoring companies. Requirements on content may have negative effects on company’s efficiency, revenue and profit growth.
For long-term, the Opinion has positive effects to make tutoring sector more regulated and healthier, but companies must adapt and incorporate voluntarily.
Inconsistency between the Draft and the Opinion
There is some inconsistency between the Draft and the Opinion. Since the Opinion is officially issued, thus it is more likely the Draft will follow and be consistent with the Opinion in the future version.
Regulation effects on New Oriental
After the release of the Opinions and the Draft, the ambiguity and uncertainty in the both regulations spooked the market and caused shares of oversea-listed Chinese education companies plunged for more than two months including New Oriental.
Although requirements on content may have negative effects on efficiency, revenue and profit growth in general for each player. The Opinion’s strengthening requirements will have biggest pressure on small tutoring companies and raise the entry barrier substantially. This strengthening measure, if implement equivalently, can push consolidation further and squeeze out large number of small players.
If Matthew effect can show up as the sector consolidates further, then it is a good opportunity for big players like New Oriental to occupy more market share from small players. If New Oriental is able to seize more make share, then the company can actually benefit from the regulation.
Other information:
VIE structure:
The variable interest entity (VIE) structure is a common approach that Chinese companies use for offshore listing. But why don’t Chinese companies seek for onshore listing? The main reason is the different IPO systems between China and oversea markets.
Currently China still uses approval-based IPO system while US uses registration-based initial public offering (IPO) system. Therefore, when a Chinese company decides to seek A-share listing, it will always face quite high requirement and lengthy procedure. It is not hard to understand why so many Chinese companies go for offshore listing.
For offshore listing, there are two ways, direct and indirect. For direct offshore listing, approval of the China Securities Regulatory Commission is required which is also difficult. Thus, indirect offshore listing becomes a common choice.
The VIE structure is a feasible way to satisfy in legal, accounting and other aspects by both countries: the one the business entity is domicile and the one the company issues IPO.
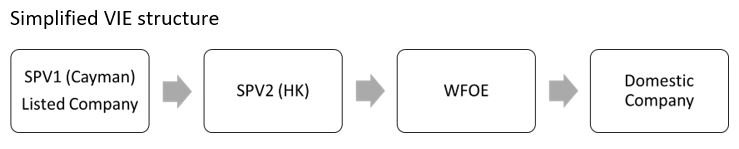
To implement indirect offshore listing, a Chinese company needs to set up an offshore company SPV1 which is the company to be listed. And then SPV1 sets up another wholly-owned SPV2 in HK for tax, trade or other convenience. SPV2 sets up the wholly foreign-owned enterprise (WFOE) in China. And the WFOE controls the actual domestic company through contractual arrangements.
The reason for controlling the domestic company through contractual arrangements is that the industries in China are classified into four categories, namely, the encouraged, permitted, restricted and prohibited. And foreign investments are restricted in education industry. A simplified VIE structure and a detailed New oriental education & technology group are presented below:
Simplified VIE structure
New oriental education & technology group VIE structure
Hidden Content
Disclosure: Yu Qian is an independent equity research analyst/writer.
This article is written by myself and it expresses my own opinions. I have no relationship with any company which is mentioned in this article.
Feel free to reach me at my correspondence below:
yuqian.chinesestocks@gmail.com; https://www.linkedin.com/in/yuqianzhou/